You are here
» » Green Infrastructure (GI): The ecological...
Green Infrastructure (GI): The ecological framework needed for environmental, social and economic sustainability
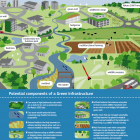
What is GI?
GI is an interconnected network of natural (e.g. waterways, wetlands, forests) and semi-natural (e.g. parks, farms, conservation lands) areas that conserves ecosystem services as well as provides additional benefits to human populations. Some benefits of ecosystem services are: carbon storage, clean air and water and pollination (European Commission 2013; Benedict & McMahon 2006).
The concept around GI is that a single area of land can offer a range of benefits provided that its ecosystems are in healthy condition. GI uses vegetation, soils and natural processes to manage water and create healthier urban environments. GI also play a key role in fighting climate change impacts as the landscape would be more resilient to floods, soil erosion and other environmental disasters (European Commission 2013; Benedict & McMahon 2006).
GI differs from other conventional approaches as it stems around “smart” conservation which deals with the ecological and social impacts of urban sprawl, fragmentation of open areas and consumption of land. For the GI network to work, long-term planning and management efforts are needed and then need to be maintained over time (European Commission 2013; Benedict & McMahon 2006).
Not so fun facts:
Read more